Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) is a destructive pest that threatens crops worldwide.
It causes significant yield losses and food security concerns. This page covers essential information about fall armyworm identification, treatment, and prevention strategies to safeguard harvests across different crops.
By understanding this pest and implementing effective management techniques, farmers can protect their crops and livelihoods from the ravages of fall armyworm infestations.
What is fall armyworm?
Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) is a voracious pest that can cause severe damage to multiple different crops.
Native to the Americas, this moth species has spread rapidly around the globe, posing a severe threat to food security in many regions, particularly in Africa and Asia. Research shows that globally fall armyworm costs farmers hundreds of millions of dollars every year in lost yields.
The fall armyworm gets its name from its behavior. Like an army it marches across fields in large numbers, consuming everything in its path.
This pest is particularly problematic for multiple reasons:
- Rapid reproduction: Female moths can lay up to 1,000 eggs in their lifetime.
- Wide ranging: It can feed on over 80 plant species, including major crops such as corn, cotton, rice, and sorghum.
- Migratory ability: Adult moths can travel long distances, spreading infestations rapidly.
- Adaptability: Fall armyworms can quickly develop resistance to pesticides.
Understanding its lifecycle and behavior is crucial for effective management.
The life cycle of the fall armyworm consists of four stages:
- Egg: Females lay eggs in masses on the underside of leaves.
- Larva: The caterpillar stage, lasting about 14-21 days, is when most crop damage occurs.
- Pupa: The transformation stage, typically occurring in the soil.
- Adult: Moths emerge and begin the cycle again.
Recognizing these stages and understanding the pest's behavior is extremely important for implementing timely and effective fall armyworm treatment and prevention strategies.
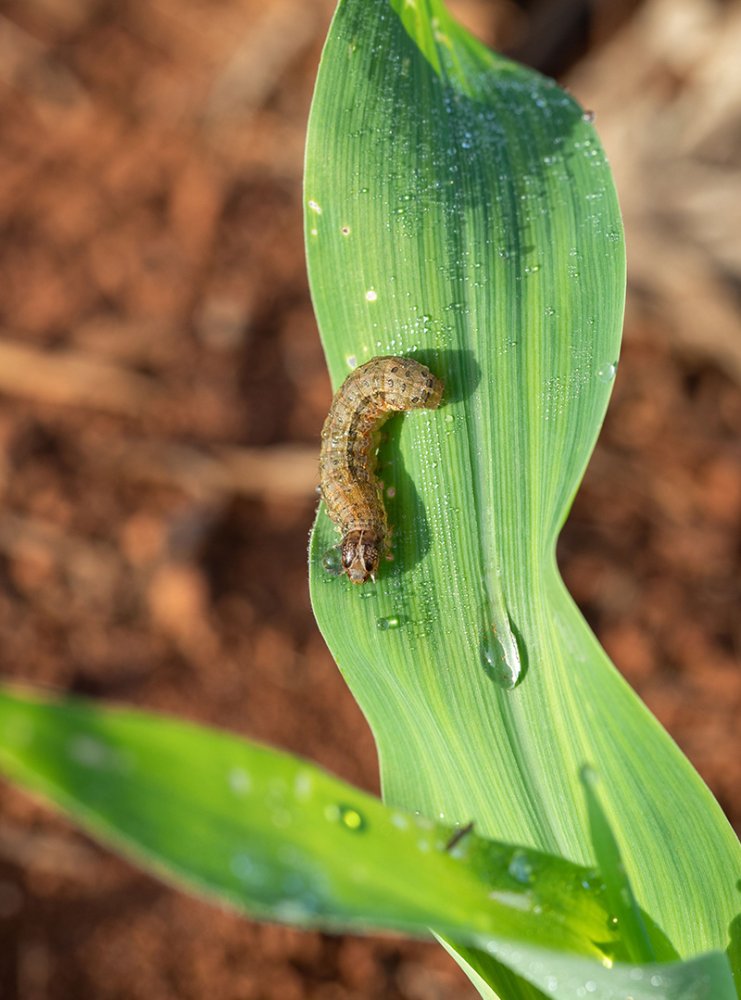

What are the typical symptoms of fall armyworm?
Identifying fall armyworm damage early is the key to successful treatment. Farmers and agricultural professionals need to be vigilant in monitoring their crops. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Irregular holes in leaves: Fall armyworm larvae feed voraciously, creating irregular patterns of damage on leaves.
Skeletonized foliage: In severe infestations, leaves may be completely stripped, leaving only the veins.
Damage to crop ears or fruits: In crops like corn, fall armyworms can burrow into the ears, causing significant damage.
Clusters of caterpillars: Fall armyworms often feed in groups, especially in the early stages of infestation.
Window paning: Young larvae may feed on one side of the leaf, leaving a transparent layer that resembles a window.
Whorl damage: In crops like corn, fall armyworms often target the whorl, causing distinctive damage patterns.
Silk clipping: In corn, larvae may feed on silks, potentially interfering with pollination.
Stunted plant growth: Severe infestations can lead to overall plant stress and reduced growth.
Ragged leaf edges: As larvae grow larger, they consume entire leaf sections, leaving ragged edges.
The global spread of fall armyworm
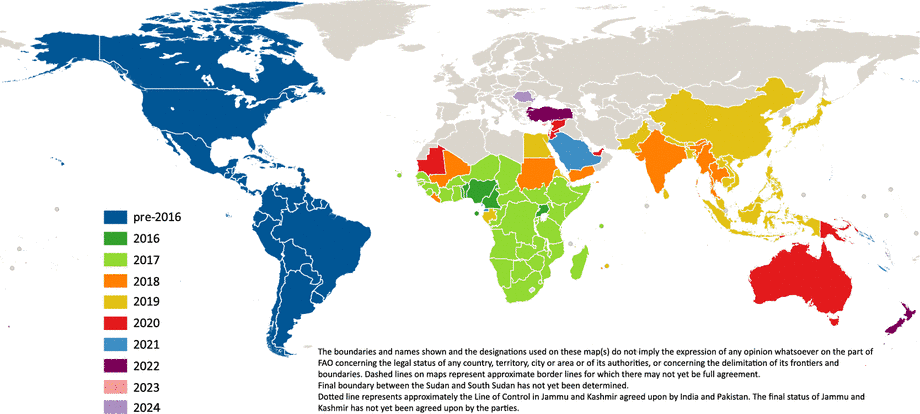
The worldwide spread of fall armyworm since 2016 (as of July 2024). Credit: The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
A billion dollar problem
Fall armyworm is one of the most invasive pests threatening global food security and control options can vary across different countries, cropping systems and ways of working. Find out how innovative science is taking on one of the world’s most disruptive pests.
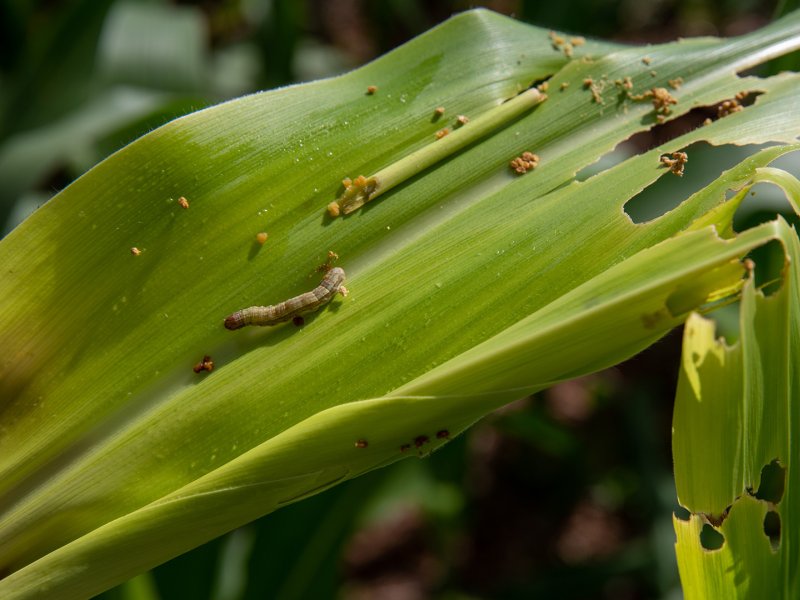

How can fall armyworm be prevented?
Preventing fall armyworm infestations is always more cost-effective than treatment. Currently no country with fall armyworm has managed to entirely eradicate the pest. However, the following strategies can be useful as preventative strategies:
• Many regions around the world use early warning systems and regular scouting
• Practice crop rotation
• Encourage natural predators through habitat management
• Make the most of resistant crop varieties when available
• Invest in preventive seed treatments
• Use pheromone traps for monitoring pest populations
Fall armyworm treatment
Different crops require tailored approaches for effective fall armyworm management. Here are some recommendations for the most at risk crops.
-
Corn
Corn is grown world-wide and is particularly vulnerable to fall armyworm infestations. Effective treatments include:
- Targeted insecticides: Apply during early infestation stages, focusing on the whorl where larvae often feed.
- Biological control agents: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) products can be effective, and especially useful for organic production.
- Pheromone traps: Use these for monitoring pest population levels and timing interventions.
- Push-pull technology: Intercrop corn with plants that repel fall armyworm (push) and plant attractive trap crops around the field (pull).
- Use a corn hybrid with a Bt trait stack that has inherent pest resistance.
-
Cotton
Cotton can require a nuanced approach to fall armyworm treatment and regular observation is crucial:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies: Combine cultural, biological, and chemical control methods.
- Use products that target lepidopteran pests while preserving beneficial insects.
- Make sure to rotate insecticide classes to manage resistance.
- Bt cotton varieties: Consider planting cotton that expresses Bt proteins for inherent pest resistance.
-
Soya
Fall armyworm treatment in soya requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Scouting: Regularly inspect soya fields, focusing on leaf damage and the presence of egg masses or young larvae.
- Timing: Apply treatments in the early morning or late evening when larvae are most active.
- Biological Control: Encourage natural predators like parasitic wasps and birds, bats and other predatory bugs.
- Resistance Management: Rotate insecticide modes of action to prevent resistance development.
Syngenta solutions for fall armyworm
Local regulations and approvals will determine which products are available in your region but Syngenta’s powerful and effective solutions to fall armyworm include:
- Duracade Viptera™: An industry-leading trait stack that delivers leading above and below ground protection from multiple threats, including fall armyworm.
- Fortenza® Duo: A seed treatment providing early-season protection.
- Ampligo®: A foliar insecticide for rapid control of fall armyworm.
- Proclaim®: An effective solution for controlling lepidopteran pests.
- Karate Zeon®: A broad-spectrum insecticide for fall armyworm control.
- VERDAVIS 250 ZC: A broad-spectrum insecticide for fall armyworm control.
Find out more about our disease management solutions in your region

